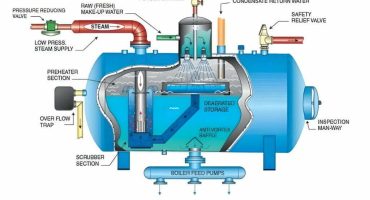
Steam Boilers are undoubtedly an essential asset in the process and manufacturing facilities. However, it is imperative to take every measure in ensuring the proper functioning of the steam boiler for optimal productivity. Boiler water and its quality play a vital role in hassle-free operations of the boiler system. Similarly, neglecting the boiler water quality results in damaging the steam boiler components, consequently leading to boiler failure. Hard water can negatively impact the performance of the steam boiler. Hard water consists of a higher concentration of dissolved minerals like calcium and magnesium. Let us learn about hard water in detail to understand it better.
Difference between hard water and soft water:
As mentioned, hard water includes a higher concentration of dissolved minerals, particularly calcium and magnesium. Water from the treatment plant consists of small amounts of dissolved solids such as calcium and magnesium, damaging the tubes in the steam boilers. The minerals can lead to hard scale buildup on the tube surface, resulting in reducing the water heat transfer and overheating the tubes.
On the other hand, soft water has relatively less calcium and magnesium but higher dissolved sodium. Therefore, water softening units utilize sodium pellets for hard water softening by exchanging the calcium for sodium.
Hard Water and Steam Boiler:
Hard water causes several problems in steam boilers. It is due to the dissolved ions left behind as the water is heated to the steam. The leftover ions bond and form calcium carbonate, also known as limescale. The limescale covers pipes and other components of the steam boiler.
- Suspended solids:
Suspended solids are substances present in water as suspended particles, usually minerals. These substances are not a significant issue as they can be filtered out.
- Dissolved solids:
As the name suggests, dissolved solids are substances that dissolve in water, primarily including carbonates and sulfates of calcium and magnesium that form scale when heated. In process operations, it is necessary to examine any salts that form scale in the steam boiler that should be altered chemically to produce suspended solids or sludge instead of scale.
- Dissolved gases:
Dissolved gases include oxygen and carbon dioxide that is dissolved easily by water. The gases are major contributors to corrosion.
- Scum forming substances:
It includes mineral impurities that foam or scum, such as soda in the form of carbonate, sulfate, or chloride.
The impurities present in boiler water are less and generally expressed in water analysis as parts per million (ppm), by weight, or in milligrams per liter (mg/l).
Identifying Hardness in Water:
Water used for steam boilers is either hard water or soft water. It is differentiated by the impact of water on the soap as a higher amount of soap is required for making lather with hard water compared to soft water. Hardness results from the mineral salts of calcium and magnesium that lead to scale formation.
The hardness is further classified into two types:
- Alkaline hardness or temporary hardness:
Alkaline hardness, also termed as temporary hardness, is caused due to the presence of calcium and magnesium bicarbonates. The salts dissolve in the boiler water and form an alkaline solution. As the heat is applied, it decomposes to release carbon dioxide, scale, and soft scale. It is termed temporary hardness because the hardness is removed by boiling.
- Non-alkaline hardness and carbonates or permanent hardness:
Non-alkaline hardness is caused by the salts of calcium and magnesium, although in the form of sulfates and chlorides. As the temperature increases, it precipitates from the solution, due to its reduced solubility and forms a hard scale that is difficult to remove.
Additionally, the silica in the steam boiler water leads to a hard scale that reacts with calcium and magnesium salts and forms silicates that severely cover the heat transfer across the fire tubes, causing it to overheat.
Total hardness:
Total hardness is not a type of hardness, but the total concentrations of calcium and magnesium ions present when both expressed as CaC03. With alkaline water, a proportion of hardness that is equal in magnitude to the total alkalinity, also expressed as CaC03, is considered as alkaline hardness, and the remaining as non-alkaline hardness.
Non-scale forming salts:
Non-hardness salts like sodium salts are relatively more soluble than the salts of calcium or magnesium that do not generally form scale on the surfaces of a steam boiler.
Comparative units:
As salts dissolve in water, it forms electrically charged particles termed ions.
The metallic parts (calcium, sodium, magnesium) are cations, attracted to the cathode, carrying positive electrical charges. On the other hand, anions are non-metallic, carrying negative charges like bicarbonates, carbonate, chloride, sulfate that get attracted to the anode.
pH Value:
pH value is a numerical value indicating the hydrogen content of water that determines the measure of the acidic or alkaline nature of the water. Water, H2O, includes two types of ions – hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxyl ions (OH-).
With predominant hydrogen ions, the solution is acidic with a pH value between 0 and 6. However, with higher hydroxyl ions, the solution is alkaline with a pH value between 8 and 14. An equal amount of hydroxyl and hydrogen ions results in a neutral solution with a pH value of 7. Acids and alkalis can increase the conductivity of water above the neutral sample.
Prevention for Hard Water:
The ideal solution for the issue of hard water is a water softener in the steam boiler. Water softeners introduce sodium compounds into the steam boiler for the removal of calcium and magnesium and reduce hard scaling in the steam boiler. It improves the water flow, increases efficiency levels, and prevents failures or damages that can reduce boiler lifespan.
It is equally important to schedule regular boiler maintenance to prevent the build-up of the limescale.
Rakhoh Boilers are a trusted name for boiler manufacturing and thermal solutions since 1983. We provide efficient steam boilers, waste heat recovery boilers, thermic fluid heaters, boiler accessories, and boiler services in over 26 countries globally.
For more information, visit www.rakhoh.com