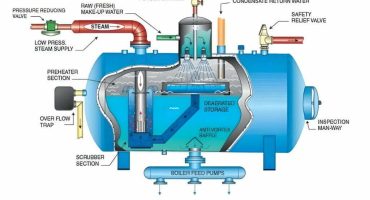
Role And Types Of Soot Blowers In Steam Boilers
Steam Boilers are essential for operational processes in manufacturing industries. If left neglected, boiler issues can hinder the seamless operation. One such boiler issue is soot formation. Soot is a carbon-based material that accumulates as a byproduct of combustion and sticks to the walls and surfaces of the steam boiler system during operation. Soot is a natural insulator that makes it challenging for conducting heat efficiently. As a result, it reduces the steam boiler efficiency by blocking some heat from passing through the system. Additionally, soot can lead to fires and damage the boiler system if not cleaned properly.
What Are Soot Blowers?
A soot blower is boiler equipment for eliminating the soot deposits within the steam boiler to keep it running safely and seamlessly. Different soot blowers are used in the different components of the industrial boiler, each with unique advantages. The two major mediums for removing soot are compressed air and steam, with steam being more preferred as it has a lower cost than the expense required for compressors, motors, and control of air systems. Once the soot is removed, it is passed through the system by flue gas and leads to a dust collector or expelled through the smokestack.
Problems Caused By Soot Formation:
When a steam boiler or furnace is operating for a long period, it causes more deposits on all its heating surfaces. Soot in a furnace or other burning equipment lowers efficiency and may also lead to fire hazards. Firstly, a soot coating in the boiler system acts as an insulator that reduces heat exchange, and thus more energy is required for achieving optimum temperature. Secondly, excessive soot can catch fire, resulting in risk or damage to the equipment, surrounding area, and personnel.
Types of Soot Blowers:
Wall Soot Blowers:
A wall soot blower is one of the basic types of soot blowers. It is a small piece of equipment that is connected to the exterior of the boiler. A short nozzle that enters the steam boiler releases hot steam or compressed air for cleaning the surrounding area. The nozzle retracts while not operating, making the wall blower an ideal choice for areas that face the issue of high temperatures.
There are various pros and cons of wall soot blowers due to their basic design. The primary advantage is that wall blowers are often smaller in size, taking less space in the area around the steam boiler. Consequently, the disadvantage is that the wall soot blower is capable of cleaning only a small section. Most industrial boilers require several wall blowers and may use other types of soot blowers to clean the accumulated soot.
Air Heater Soot Blowers:
Air heater soot blowers are ideal for cleaning the air heaters of the boiler system. As time passes, the moisture starts accumulating at the cold end of the air heater as the flue gas temperature reduces to below the condensation point. The moisture combines with soot and other byproducts and forms a fine-grain deposit.
Air heater soot blowers are installed on the cold end of the air heater and include retractable blowers or blowers with nozzles on swinging arms. The device moves across the air heater, while the swinging arm moves in an arc across the face of the heat transfer surface, cleaning a sufficient area.
Long Retractable Soot Blowers:
A long retractable soot blower extends a long lance or nozzle into the boiler. The long retractable soot blower begins at the start of the steam boiler and gradually moves through it, rotating 360 degrees to eliminate soot from every surface. The primary advantage of the application is that a single device is capable of cleaning a much larger area than a wall blower. Covering a large area reduces the total number of blowers necessary to remove soot in your boiler, simplifying the system. However, a long retractable soot blower needs to store the long lance and usually takes up considerably more space than a wall blower.
Rotary Soot Blowers:
A rotary soot blower is fixed to the steam boiler system and does not retract like other types of blowers. On the contrary, the blowing tube or element of the blower remains in the steam boiler at all times. The tube is usually equipped with several nozzles and rotates to clean a large portion of the boiler system.
As it does not retract, rotary soot blowers are not to be used in the high-temperature areas of the boiler. Rotary soot blowers are best suited for the superheater, economizer, and air heater.
Applications of Soot Blowers:
Soot Blowers Safeguards Furnace Tubes and Shells
A soot blower reduces the possibility of soot fire. Such accidents can lead to the appearance of hotspots in the furnace tubes that can later reach a temperature to weaken the structure of the tubes. The dangers of a weakened furnace structure are extreme.
Soot Blowers Enhances Operational Efficiency
Soot is a heat insulator. Therefore, more soot inside equipment leads to more energy required to get the equipment up to optimal operating temperature. As no processing plant aims to waste energy, it is too expensive.
Fuels used for combustion in steam boilers lead to various by-products coating the heating surfaces. It is accumulated on walls, screens, reheaters, etc., and every component is plastered with soot reducing energy efficiency. A soot blower is crucial for maintaining efficiency.
Conclusion:
Rakhoh Boilers is one of the trusted boiler manufacturers in Pune since 1983. With 39+ years of experience and expertise in thermal solutions, we deliver highly efficient and reliable industrial steam boilers, waste heat recovery systems, thermic fluid heaters, and boiler accessories to over 20 process industries in 27 countries worldwide. We provide excellent boiler services to boost the efficiency and productivity of the boilers.
Visit www.rakhoh.com for more details on our products and services
- Published in Boiler, Steam Boiler
Managing Low Water Levels in Steam Boilers
Although steam boilers are imperative in the process and manufacturing industries, it is also a proven fact that it has the potential of explosive bomb. As water is vital for steam generation, it is also an essential factor that may harm the boiler system. Low water conditions are one of the leading causes of boiler incidents. It is necessary to keep water levels under check to ensure safe boiler operations. Low-water level conditions in the steam boiler take place when the water in the boiler drum drops below the low water level mark. It causes the potential to damage the boiler severely.
What is the Low Water Level in Steam Boilers?
A low water level in a steam boiler occurs when the water level falls below the lowest water level mark or even below the top of the tubes, consequently leading the tubes to overheat. If the water reaches a lower level than the main firing tube, it may fail the steel itself. However, it can be prevented with proper steam boiler maintenance.
As the furnace temperatures generally exceed 1,800°F (980°C), the strength of the steel falls significantly at temperatures above 800°F (480°C). Therefore, low-water levels may cause the melting of the steel tubes. As water enters an exceedingly overheated boiler, the water flashes to steam. The impacted metal parts rupture due to the sudden increase in pressure, causing a steam explosion.
Effects of Low Water Level in Steam Boiler:
One of the most hazardous cases of low water takes place when the water is added to the steam boiler, but the system has already passed the point of no return as the boiler vessel is extremely overheated. It causes the water to quickly turn into steam, resulting in tremendous pressure and the explosion of the steam boiler system. It is one of the most dangerous results for any boiler system and must be prevented.
Commonly found damage caused by low water levels includes:
Controlling Water Drum Level:
Controlling the boiler drum level is challenging as the water level in a steam drum is, in fact, an unstable combination of water and steam bubbles that shrinks and swells with the changing pressure. The increasing steam demand reduces the pressure in the boiler, causing the water level to rise. Additionally, as the freshwater enters from the feed tank and cools the drum water, it leads to the collapse of the steam bubbles and a drop in the water level. The solution for the shrink and swell effect in the steam boiler is opting for a 3 level drum control.
Low water conditions result from both operator and equipment issues. Some of the common causes include:
Low Water Cutoff Device:
Steam boilers are installed with low water cutoffs to prevent any significant damage. The devices operate to identify the low water condition and shut down the boiler system. The burner remains off till the water returns for the burner to fire normally.
Some low water cutoff devices serve the dual function of starting and stopping feedwater flow and stopping the burner. Such a device is known as the Primary Low Water Cutoff Device. A Secondary Low Water Cutoff Device serves another purpose of initiating a safety shutdown and lockout.
Failures in Low Water Cutoff Device:
Low Water Cutoff Devices are usually very reliable and well-functioning. However, the following factors can result in a breakdown.
Deposits: Condensate water and new make-up water enters a steam boiler and deposits minerals and solids.
Outdated models: Most boiler manufacturers recommend periodic replacement of the mechanical components of the steam boiler system. If overlooked, outdated boilers can lead to leaks and parts failure.
Loss of Water: Steam leaks and faulty steam traps requiring a high amount of makeup water cause issues in steam boilers and Low Water Cutoff Devices from loss of water. In such situations, the entire system requires proper maintenance.
Jumpers: At times, jumper wires are used temporarily for diagnosing a problem or bypassing a circuit for testing. If ignored, the Low Water Cutoff Device fails to shut down the burner.
Maintenance: Proper boiler maintenance needs the purging of the Low Water Cutoff Device system. It requires attention as improper flushing can also cause damage.
Conclusion:
As one of the world’s leading combustion experts and boiler manufacturers, Rakhoh specializes in thermal solutions. We have more than 39 years of experience in designing and manufacturing steam boilers and boiler accessories. Rakhoh offers a range of high-quality steam boilers that are compatible with a variety of fuels and applications.
For more details on our products and services, visit www.rakhoh.com
- Published in Boiler, Steam Boiler
Leakage in Steam Boilers and Preventive Measures
Steam Boilers are pivotal in manufacturing and process industries for heating and processing purposes. Although steam boilers are essential in industries, the maintenance of the boiler system is an important and challenging task for plant managers. One of the major steam boiler maintenance issues is boiler leakage. Boiler leakage should never be overlooked as it may lead to hazardous consequences such as corrosion of boiler components. Boiler leakages are found primarily during the winter season. It is because of the steam boiler operating overtime. As the temperature falls below zero, the water in the pipes and inside the steam boiler freezes into ice. Additionally, the condensate pipe removing the remaining steam and condensation from the steam boiler can freeze shut, hindering the steam boiler from functioning properly.
Detecting Boiler Leakages:
Determining boiler leakage helps in understanding the root cause of the leakages. It may be caused due to steam boiler pressure being too high or due to the pressure relief valve. Boiler leakages can be detected by
Causes of Boiler Leakages:
Let us learn some of the common causes of boiler leakages that can lead to the best course of action before causing any severe damage to the steam boiler system,
Pump:
The pump is a vital component of the steam boiler that constantly runs and circulates water in the entire boiler system. Due to its continuous operation, the pump valve or seal can break easily as the rubber seals are hardened or destroyed by elements passing through the steam boiler system.
The repair depends on the extent of damage caused to the pump. One solution involves resealing the pump with a gasket kit, while another solution suggests entirely replacing the boiler pump.
Pipes:
The pipes circulate water throughout the steam boiler system. Therefore, the pipes leading in and out of the steam boilers are possibly the reason for the boiler leakages. It is mostly due to improper installation or the degradation of pipe connection caused by corrosion over time. Both the issue requires the replacement of the component and proper installation.
Pressure Relief Valves:
The pressure relief valve safeguards the steam boiler system from generating excess pressure. During extremely high pressure, the steam boiler releases steam and water. Such situations can result in significant damage, and therefore, it is important to detect and address faulty valves as soon as possible. Pressure relief valves are repaired by removing lime or debris or resealing the valve.
Corrosion:
The rusting and corrosion in the boiler vessel deteriorate the boiler system and lead to water leakage. It is likely that the corrosion detected signifies an outdated steam boiler that needs immediate replacement. On the other hand, it is also possible that the corrosion is caused due to poor water quality.
A feedwater treatment system removes the harmful impurities, contributing to the build-up of scale in the steam boiler as well as the piping and fittings. Scaling in the steam boiler internals, safety equipment, and auxiliary piping indicates poorly treated feedwater.
Thermal Fatigue:
Thermal fatigue is usually caused due to improperly regulating feedwater temperatures and quality, resulting in boiler leakages. It is essential to assess the feedwater and examine if the feedwater temperature is too low as it leads to thermal shock cracking the welds in an area where the hot boiler water is introduced to the low-temperature feedwater. One of the primary issues internally of the steam boiler is the reduction of heat transfer to the components.
As the boiler tubes and tube sheets are the mediums between the hot combustion gases and the boiler water, the scale build-up can significantly reduce the heat transfer rate. It is because the scale acts as an insulator instead of a conductor. The reduction of heat transfer rate leads to overheating of the boiler components, causing metal fatigue and failure. It is mainly found in cases of cracks, ruptures, or complete boiler failure. Overlooking these issues can eventually result in boiler failures.
Preventive Measures for Boiler Leakages:
Short-Term Preventive Measures:
In some of the causes of boiler leakages, a simple fix is enough to avoid the leakages. If the water is leaked due to issues in the pump and pipes, resealing or replacing the part is ideal prevention. It is an easy and immediate fix that helps the steam boiler operate as soon as possible.
Long-Term Preventive Measures:
In certain situations, it is essential to replace the entire steam boiler system if the boiler leakage is caused by rust or corrosion. It indicates that the boiler is outdated and may fail in operating despite any short-term repairs.
Regular Maintenance:
Regular maintenance is the best method to avoid issues like boiler leakages by determining the cause at the initial stage before it can cause any damage to the steam boiler.
Conclusion:
Since our inception in 1983, Rakhoh Boilers have emerged as a leading boiler manufacturer in India and Overseas with 3000+ successful boiler installations in over 26 countries. Our product range includes efficient and reliable industrial steam boilers, waste heat recovery systems, thermic fluid heaters, and boiler accessories. We also provide excellent boiler services like energy audit, steam trap assessment, boiler automation, annual boiler maintenance, etc., to ensure the efficiency and productivity of steam boilers.
For more details, visit www.rakhoh.com
- Published in Boiler, Steam Boiler
Know the History and Evolution of Steam Boilers
Think about the world without steam. Transportation and communication were difficult, commerce was outdated, and processing industries were unheard of. The invention of the steam engine was an integral part of the industry during the Industrial Revolution. The term steam boiler is used to refer to heat generation. However, it is also applied to any type of equipment that heats water and stores or uses the steam for a specific purpose. The majority of steam boilers are considered high-pressure boilers. Pressure builds as large quantities of steam accumulate inside a contained vessel. When enough steam is produced, the released energy can power the moving parts of a machine.
The history and journey of advanced steam boilers found today go a long way back. Let us understand the evolution of steam usage and boiler manufacturing in the world.
The invention of the First Boiler:
It is said that the first-ever boiler existed as early as the 1st century. However, such boilers were nothing more than toys. Boiler manufacturing officially began in the 17th century as steam power was given importance for potential applications in daily life. The first steam boiler with a safety valve was manufactured in 1679 by France’s Denis Papin.
By the 18th century, steam boilers were used and manufactured in England from wrought iron. However, as the primary advantages of temperature and high pressure came into light, more and more boiler manufacturers turned to steel. The advanced steam boilers were made of alloy steel to withstand extremely high temperatures and pressures.
The History of Steam Boiler Manufacturing:
Looking at the history of steam boiler manufacturers in the USA, the first-ever steam boiler manufacturers were Steven Wilcox and George Babcock, founders of the steam-generating boiler in the U.S. The duo was the first to patent the boiler design that included tubes inside a firebrick-walled structure to generate steam.
A few decades later, in 1891, the two started the Babcock & Wilcox Company in New York. The first boilers of the company utilized lump coal and were relatively small that were fired by hand. Due to these factors, the first patented boilers by Babcock & Wilcox Company operated at an exceptionally less rate of heat input.
Introduction of Bent Tube Boilers:
As advanced technology changed the scenario, 1916 witnessed a new landmark for boilers. It was at this stage when an engineer brought improvement with bent tubes. The bent-tube discovery led to more compact boilers with an ability to handle the cold water feeds that were staples throughout this period.
Evolution of Cast Iron Bar:
As the bent tube boilers gained more popularity, the next improvement was cast iron boilers. Although bent tube boilers and fire tube boilers were ideal for delivering high-pressure steam, they also failed to provide efficient low-pressure steam for heating purposes.
However, the cast iron boiler came to be sufficiently durable for providing low-pressure steam. Although it was difficult to repair and heavy, cast iron boilers were manufactured in various types of shapes, a noteworthy change in the directional history of boilers.
Boilers in Post-War Industrial World:
During World War I and II, the marine boilers were highly dependent on the fuel steam-powered merchant ships and steam-powered combat boats. Marine boilers held an important place during the war years.
The post-war industrial world brought the need for more production from boiler manufacturers. The tube boilers were developed on a high scale. Later, the copper tube boilers gained popularity but presented a unique set of issues that required regular replacements.
Introduction of Condensing Boiler:
After the initial oil crisis in 1973 and environmental concerns in the 80s, boiler manufacturers started planning for more cost-effective solutions to minimize energy consumption in steam boilers due to an increase in energy prices. The solutions included operating boilers at lower water temperature and adjusting the water temperature in the boiler to the temperature outside. At present, condensing boilers offer an extensive range of benefits, such as:
Evolution of New Steam Boiler Design:
By the late 1970s and early 1980s, the growing disposal costs for landfills and increased demand for electric power led to the development of biomass-fired boilers. Steam boilers with fluidized bed technology were manufactured as an alternative method of burning solid fuels like coal. Depending on the boiler manufacturer, a fluidized bed boiler may include cyclones, combustion chambers, over-bed burners, collection hoppers, etc. The fluidized bed boiler involves a process through which solid fuels are suspended in an upward-flowing gas or airstream at the bottom. The burning fuel exists in a fluid-like state with a high heat transfer but reduced emissions.
Conclusion:
If you are looking for an efficient and reliable steam boiler for your process or manufacturing industry, Rakhoh is here to help. Since our inception in 1983, we have merged as the leading boiler manufacturers in the world. Our highly-skilled engineers will listen to your facility requirements and guide you to the best solution.
Learn more about our products and services at www.rakhoh.com
- Published in Boiler, Steam Boiler
Introduction to Mobrey and Its Application in Steam Boilers
Steam boilers are imperative for heating, processing, sterilizing, and power generation in manufacturing and process industries. Several factors are considered to ensure the proper functioning of the steam boilers. The water level and water quality play a vital role in hassle-free and safe operations of steam boilers. Water quality is assured by a process like a blowdown or by using water softeners, but water level requires precise management and is controlled by using mobrey. Mobrey is equipment to control the water level in the steam boilers. Let us learn more about mobrey in detail,
What is Mobrey in Steam Boilers?
Mobrey is an automatic boiler water level control included in the category of mountings and fittings in a steam boiler. Mobrey is usually found in smoke tube boilers due to its greater shell diameter compared to water tube boilers, regardless of the running capacity and working pressure of both types of boilers.
Mobrey is placed on the external of the smoke tube boilers, on the nozzles coming out of the boiler shell. It comprises a hollow cylindrical unit that hangs a float. The feed water is provided to the boiler shell by the feed pump to fill the shell. The water enters the hollow cylindrical of the mobrey through nozzles that cause the float to rise upwards.
As the steam boiler operates, the water gets heated and generates steam. As a result, the water in the boiler shell is reduced, leading to the float coming down as well. When the float covers a determined distance, the mobrey passes an electrical signal to the electrical panel that, resultantly, starts the feed pump to balance the water shortage. It causes the float to move up once again after refilling.
The coordination system between mobrey and feed pump is termed Cascade Control System. The Cascade Control System uses the output of the primary controller to influence the output of the secondary controller, as the second controller output is the required one. In this case, the primary controller is mobrey, and the secondary controller is the feed pump.
Components of Mobrey in Steam Boilers:
Modulating controller:
The modulating controller mounted on the steam boiler includes a chamber with a float and float rod attached to an actuator that moves freely up and down inside a steam tube around a mounted inductive coil A. The inductance of this coil varies by the movement of the actuator, changing in water level.
Modulating control valve:
Modulating control valve is placed in the boiler feed water line with an actuator and inductive coil B. The inductance of this coil varies by the movement of the valve spindle. The feedwater flow to the steam boiler is controlled by the modulating valve lid, operated by a piston, actuated by two solenoid valves on the modulating valve. The inlet solenoid valve allows water at feedline pressure to the cylinder and piston, reducing the modulating valve opening. The exhaust solenoid valve releases water from the cylinder and piston to increase the modulating valve opening.
Control box:
The control box includes a circuit board connecting mains input, solenoid valves, sensing coils, and the low-level alarm/burner cut-out functions. The control box identifies any difference in inductance balance between the modulating controller, thereby letting the appropriate solenoid valve to open.
Application of Mobrey in Steam Boilers:
Automatic cold start conditions:
It is utilized for all pumps capable of operating against closed discharge. With an increasing water level in the steam boiler, the modulating valve lid is decided by the capacity of the steam boiler.
Rising water level:
As the float rises, the actuator changes the inductance at coil A the control box detects the change and opens the inlet solenoid valve that allows feed pump pressure onto the piston to move the modulating valve lid downwards, reducing the flow of water into the steam boiler. The modulating valve continues its downward movement until the inductance at coil ‘B’ is in balance with coil ‘A’. The control box closes the inlet solenoid valve to lock the modulating valve in its new position.
Falling water level:
The falling water level is the reverse of the rising water level sequence, with the outlet solenoid valve releasing hydraulic pressure from the piston, causing the modulating valve to open. It results in increasing the flow of water to the steam boiler.
Conclusion:
Mobrey is essential equipment to maintain the water level in the steam boiler to enhance its overall safety in process operation by reducing manual intervention.
Rakhoh Boilers have been consistently contributing to the thermal sector since their inception in 1983. We have manufactured and successfully delivered our efficient and reliable steam boilers, waste heat recovery boilers, thermic fluid heaters, and boiler accessories in over 26 countries worldwide.
Learn more about our products and services at www.rakhoh.com
- Published in Boiler, Steam Boiler