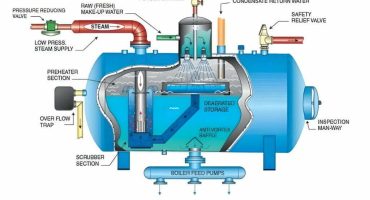
Efficiency is an important factor in evaluating the performance of the boiler. The overall boiler efficiency depends on the efficiency of the various other components. The boiler efficiency is mainly determined by its combustion and thermal efficiency. It can be affected by some other losses as well.
Combustion Efficiency:
The combustion efficiency determines the burner’s ability to burn the fuel. The combustion efficiency is indicated by the amount of unburned fuel and oxygen level in the exhaust. Combustion efficiency depends on the fuel burned and is higher for liquid and gaseous fuels than solid fuels.
Thermal Efficiency:
Thermal efficiency indicates the effectiveness of the heat exchanger to transfer the heat energy in the boiler. Scaling and soot formation on boiler tubes negatively impact thermal efficiency.
Boiler Efficiency Testing:
Apart from combustion efficiency and thermal efficiency, other parameters affect the overall efficiency, such as blowdown losses, on-off losses, convection losses, radiation losses, etc. Boiler efficiency is calculated through two methods,
Direct Method: The direct method of testing boiler efficiency involves comparing the energy of the fluid (water and steam) with the fuel energy
Indirect Method: The indirect method of testing efficiency determines the difference between the losses and the energy input in the boiler
Direct Method of Testing Boiler Efficiency:
The direct method is also termed as input-output method as it only requires output (steam) and input (fuel) to assess the boiler efficiency and can be calculated by the following formula,
Boiler Efficiency = (Heat Output/Heat Input) x 100
Measurements Required for Direct Method Testing of Efficiency:
Heat Input:
Both heat input and heat output are imperative for calculating efficiency. Heat input measurement requires the calorific value of the fuel and its flow rate in terms of mass or volume, depending on the fuel.
Solid fuel: Measuring an accurate flow rate of coal or any other solid fuel is challenging. Measurement based on mass requires an apparatus set-up in the boiler house. The sample bags are sealed and sent to laboratories for testing.
Liquid fuel: Heavy fuel oil is viscous that causes it to vary with temperature. The meter installed in the combustion appliance provides approximate results, and it is advisable to use a calibrated meter for the particular fuel.
Gaseous fuel: A gas meter used requires the measured volume to be corrected for temperature and pressure.
Heat Output:
Various methods are used to measure heat output. Steam boilers use the installed steam meter to measure the flow rate. With small boilers, feed water can be measured by calibrating the feed tank. Heat addition used for conversion of feed water to inlet steam must be considered for heat output. Additionally, the heat loss during continuous blowdown should be calculated and included in the steam heat.
Advantages of Direct Method of Testing Boiler Efficiency:
- Quick evaluation of efficiency
- Needs few factors for calculation
- Requires less instruments for testing
Disadvantages of Direct Method of Testing Boiler Efficiency:
- Causes of low efficiency remain unspecified
- Does not calculate various losses at different stages
- Wet steam due to carryover may lead to incorrect evaporation ratio and efficiency
Indirect Method of Testing Boiler Efficiency:
The indirect method includes measuring all the losses that take place in the boiler. The efficiency is calculated by subtracting heat loss from 100. Unlike the direct method, slight measurement errors would not significantly change the efficiency rate in the indirect method. The various types of heat losses in boilers are losses due to hydrogen in fuel, dry fuel gas, moisture in fuel, carbon monoxide, air moisture, convection, surface radiation, unburned losses in fly ash and bottom ash, etc.
Boiler efficiency can be calculated by the indirect method of testing with the following formula,
100 – Losses occurred in the boiler
Measurements Required for Indirect Method of Testing Boiler Efficiency:
The parameters required to measure boiler efficiency through the indirect method are as follows,
- Flue gas analysis in terms of percentage of carbon dioxide, oxygen, and carbon monoxide in flue gas, and temperature of flue gas
- Flowmeter measurements for feed water, condensate water, fuel, steam, and combustion air
- Temperature measurements for fuel, makeup water, steam, flue gas, combustion air, feed water, and condensate return
- Pressure measurements for fuel, steam, draft, and combustion air (primary and secondary)
- Water conditions for Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), Blowdown rate, and pH
Advantages of Indirect Method of Testing Boiler Efficiency:
- Complete balance between mass and energy for individual stream
- Alternatives to improve boiler efficiency are identified
Disadvantages of Indirect Method of Testing Boiler Efficiency:
- Requires considerable time
- Needs lab settings for analysis
Factors that improve boiler efficiency:
- Regular maintenance of boilers
- Excess air control
- Quality of Fuel
- Boiler insulation
- Proper water treatment
- Optimal steam pressure and temperature
Rakhoh Boilers are one of the reputed steam boiler manufacturers and service providers in India and worldwide. With 38+ years of experience, we deliver world-class quality boilers and the best boiler services to our clients for enhancing efficiency and productivity. To learn more about our products and services, visit www.rakhoh.com