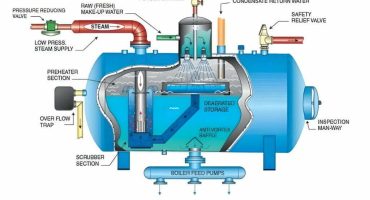
An Overview of Air Venting in Steam Boilers
Steam Boilers are the backbone for processing operations in industries. Steam in boilers is generated by the combustion of fuel that heats the water for steam production. The operating personnel in process plants take every measure to ensure that the steam boiler is operating safely, without any hindrance. However, some boiler issues are inevitable that require immediate action once detected. Air vent is one of such issues of steam boilers. When air is mixed with steam by flowing with it, the air pockets remain at the heat exchange surfaces. The steam condenses, leading to a thin layer building up and forming an insulating blanket, resultantly hindering heat transfer.
What is Air Vent in Steam Boilers?
Air is usually used in the steam boiler as an insulator due to its low conductivity. Air is also used for reducing the heat loss from steam pipes. In most cases, the insulating material consists of microscopic air cells. The air is found in the insulator while the solid material retains its position. The film of air on the steam side of a heat transfer surface shows resistance to the heat flow, reducing the heat transfer rate. With the addition of air to the steam, the heat content of the mixture is less than the same volume of pure steam. Therefore, the mix temperature is reduced.
The air present in the steam boiler has a dual impact:
- It is resistive to heat transfer through its layering effect.
- It reduces the steam space temperature, leading to reducing the temperature gradient throughout the heat transfer surface.
Why is Air Vent Important in Steam Boilers?
During the shutdown in steam boilers, the steam and condensate are eliminated from the steam boiler system, causing the space inside to be occupied by air. A minimal amount of air and other condensable gases enters the boiler with the steam. In the next operational cycle, air and non-condensable gases should be eliminated from the steam boiler, as it causes severe impacts on process operations and equipment like more warm-up times and reduced efficiency and performance. Therefore, an air-vent is essential to remove the air trapped in the process equipment.
Effects of Improper Air Vent in Steam Boiler:
- Reduction in heat transfer rates and productivity:
Air is highly resistant to heat transfer than the metal wall. Compared to iron or steel, air shows more than 1500 times resistance to heat transfer and around 13000 times more resistance than copper. Therefore, a 0.5 mm film of air offers the same amount of resistance to heat transfer that a 6.5 m copper would.
- Malfunctioning of traps:
Air in the condensate tremendously impacts the performance of traps. The condensate removal capacity of steam traps depends on the air and other non-condensable gases present in the condensate that can cause waterlogging if overlooked. It impacts the time required for process operations and product quality. Traps with air venting are ideal than other traps to avoid any issues in the steam boiler.
- Increased corrosion:
As air includes gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide that cause the corrosion of the metal walls and equipment, air can lead to high corrosion in the steam boiler. When carbon dioxide dissolves in water, it forms carbonic acid that is highly corrosive. Corrosion in steam boilers may remain undetected, causing a sudden, unexpected failure.
- Reduction in steam pressure:
The pressure applied by gas or a mixture of gases is determined with Dalton’s law of partial pressure. The law states that the total pressure of a mixture of ideal gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases in the mixture.
Therefore, the actual steam pressure is less than the pressure displayed on the gauge. With the air inside the steam, the actual pressure is less than that displayed in the gauge. Consequently, the temperature of the steam boiler will be less than required for the process operation. The lack of an optimal amount of pressure leads to a longer duration of process operation.
Signs of Air in Steam Boilers:
It is paramount to eliminate air from the steam boiler. Some indicators for the presence of air in steam boilers are as follows,
- A drop in the output of the steam boiler
- Condensate with air bubbles.
- Corrosion in the steam boiler.
Air Removal from Steam Boilers:
- Device for Air Vent:
Automatic devices are the most effective method of air removal. With the blend of air with steam reducing the mix temperature, it facilitates the thermostatic device to vent the steam boiler. An air vent installed on the steam space of a vessel or at the end of a steam main opens with air present. In order to carry the discharge and prevent it from entering a condensate return line that restricts the free release of air and causes corrosion, steam boilers are fitted with pipes.
As an air vent is fitted to a steam trap, it acts as a steam trap after the air vent, and discharges condensate. Therefore, it is necessary to reinstall the air vent to the condensate line after the trap.
- The placement of Air Vent:
A coil or a vessel with a relatively small cross-section leads to steam acting as a piston by pushing the air to a remote point from the steam inlet. The remote point is the ideal placement for the air vent.
Conclusion:
Rakhoh Boilers are the leading manufacturers of steam boilers in Pune with over 38+ years of expertise in providing efficient and reliable steam boilers and thermal solutions. Our global network is spread across 26 countries worldwide with more than 3000 successful boiler installations.
For more details on our products and services, visit www.rakhoh.com
- Published in Boiler