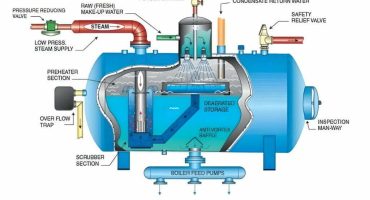
Preventive Maintenance and Cleaning of Biomass Boilers
Biomass boilers are emerging as the future of thermal solutions in the process and manufacturing industries. Boiler maintenance is an important factor to ensure hassle-free operations and optimum efficiency. In the case of biomass boilers, regular maintenance is essential to prevent the breakdown of the boiler. Regular maintenance of biomass boilers cannot be neglected as it may cause severe damage to the boiler system. It is interesting to note that the maintenance of biomass boilers varies from other conventional fossil fuel boilers due to the disposal of the ash produced in the combustion process.
Cleaning and Maintenance of Biomass Boilers:
An ideal way to assess whether the biomass boiler needs cleaning is by examining the increase in fuel consumption. The primary cause of an increase in fuel consumption is due to ash blocking the open airways of the heat exchanger and reduction of the transition of heat in the heating system.
As per the fuel quality, biomass combustion can lead to 0.5-1.5% of their weight in ash, which is released in an ash pan located beneath the grate. The ash collected needs to be removed manually at regular intervals after necessary operational cycles. The boiler maintenance intervals differ depending on the frequency of biomass boilers used for heating. Automatic de-ash systems are used to release the ash into an ash bin, thereby reducing the required amount of workload. However, the ash bin requires it to be emptied from time to time.
Another benefit of biomass boilers is that the collected ash can be used further as a fertilizer. Additionally, the chimney should be cleaned at least once every year.
Disposing Ash in Biomass Boilers:
Ash is the primary by-product of the combustion of biomass fuel. The ash generated by biomass fuel is termed potash. It is useful for the farmers as a top dressing and also for horticulturalists as a component of their compost.
Dispensing ash in such a method is highly beneficial to the environment as the nutrients from the ash are fed to aid in regenerating the wood, collected to form the fuel in the first place. It leads to the increasing popularity of biomass fuels with a boost towards the planting of trees.
Biomass boiler ash can either be disposed of as a fertilizer or landfill waste if the ash is produced in small amounts.
Biomass boilers equipped with automatic ash extraction systems usually include,
Internal ash extraction:
It includes one or more augers that pass ash from the combustion chamber into an ash pan or an external ash auger.
External ash extraction:
It includes one or more ash augers that collect ash from the internal ash augers, emptying itself into a self-contained ash bin.
Fire tube pneumatic cleaning:
It includes various hoses or pipes that automatically pass a blast of compressed air through fire tubes located on the last pass of a three-pass biomass boiler system. It is also termed as the boiler’s ‘tube nest.’
Biomass boilers equipped with the ash extraction system require a daily inspection of the boiler room. The boiler operator inspects the boiler thoroughly to ensure that the combustion levels and flue gas temperatures are within determined limits. The time required for boiler maintenance depends on the size of the boiler, fuel type, and rate of consumption.
Biomass boilers without automatic ash extraction systems need frequent shutdown and need manual servicing. The added cost of boiler maintenance and workload directly impacts by reducing fuel savings and job performance. On the other hand, biomass boilers with automatic ash extraction and tube cleaning increase the boiler performance, efficiency, and lifespan. Therefore, it is important to keep the fire tubes clean of ash for optimal efficiency. As the ash accumulates in the tubes, it acts as an insulator for heat transfer. It results in wasting the heat in the exhaust instead of exchanging it into the boiler water.
Biomass Boiler Maintenance:
Regular maintenance of a biomass boiler ensures a longer life span compared to the conventional fossil boiler system. It leads to internal combustion parts lasting long and less consumption of fuel.
Components Assessed During Biomass Boiler Maintenance:
- The internals of the heat exchanger are examined and cleaned of carbon build-up.
- The boiler and bunker feed screws are assessed and cleaned.
- Geared motor units, bearings, and seals are inspected and greased if necessary.
- Checking every safety equipment.
- Checking the ignition system.
Conclusion:
Rakhoh Boilers, are one of the trusted boiler manufacturers in India, with more than 3000 successful boiler installations in over 26 countries worldwide. We manufacture a range of efficient steam boilers that provide effective combustion with biomass boilers. We deliver waste heat recovery systems, thermic fluid heaters, boiler accessories, and various boiler services to over 20 process industries.
Visit www.rakhoh.com to learn more about our products and services.
- Published in Boiler
An Overview of Combustion Problems of Biomass Boilers and Its Solutions
Steam Boilers are irreplaceable equipment in the process and manufacturing sector industries. It produces heat through the combustion of fuel that is transferred to the water for converting it to steam at desired temperature and pressure. It is concluded that the efficiency of process industries is dependent on the efficiency of the steam boiler. The increasing fuel prices and concern towards sustainable energy production have led to the rising popularity of biomass boilers for process operations. Biomass is a type of fuel that consists of low density, bulkiness, and releases volatiles. Biomass is gaining preference for various reasons like reducing dependency on fossil fuels, more employment, and reduction in greenhouse gases and acid rain. However, there are various challenges to biomass boilers, particularly with combustion.
Combustion Challenges in Biomass Boilers:
- Agglomeration:
The issue of agglomeration is the ash-related problem, usually found in biomass boilers. Ash is formed from a high-sulfur and low-ash fuel agglomerate, with the sulphation degree varying with time and temperature. Ashes agglomerate by the production of 50–60% or more amount of calcium sulfate and Ca–K-silicates in the deposit. Initially, agglomeration occurs due to carbonation, and later due to sulfation at lower temperatures. Ash agglomeration increases with high iron or alkali metal content as the low-melting alkali chlorides promote the stickiness of fly ash particles. As a result, it increases the ash deposition on the superheater tubes. The deposited alkali chlorides contribute to the increasing corrosion of superheaters.
Solutions for agglomeration:
Agglomeration can be reduced by using additives such as sulfur, kaolin, and ammonia sulfate. Adding kaolin to the bed material before the combustion process can eliminate agglomeration. As alkali sulfates have high melting points compared to corresponding alkali chlorides, it has minimal tendency to stick to the superheaters as deposits. Therefore, it reduces the possibility of deposit formation and corrosion on the superheaters.
- Corrosion:
High-temperature corrosion is termed as the increased oxidation of materials induced by salt film deposition at accelerated temperatures on the fireside of the boiler. The increased temperature ranges from 700 to 1300 °C. High-temperature corrosion includes nitridation, flue gas, carburizing, sulphation, oxidation, chlorination, and corrosion deposit. Fused alkali sulfates are deposited on the hot substrates with the oxidation of metal contaminants such as sulfates and vanadium in the fuel.
Solutions for Corrosion:
- Inhibitors:
Corrosion inhibitors are substances that reduce the rate of corrosion of the metal. The factors for corrosion inhibition are the composition of fluid, flow regime, and quantity of water. Inhibitors are used in processing industries as it is the best defensive agent against corrosion. Corrosion inhibitors are also termed additives to the fluid surrounding the metal.
- Sol-gel coating:
Sol-gel coating is well-known for protection against corrosion as it includes better chemical stability, oxidation control, and corrosion resistance for metallic substrates.
- Varying temperature and pressure:
Findings suggest that the corrosion rate of metal doubles with every 10°C increase in the temperature. Therefore, the corrosion rate of 30 mpy (mils per year) at 30°C would increase to 60 mpy at 40°C. As the temperature increases with passive film remaining intact, it results in the corrosion rate remaining stable. However, with an increase in temperature in the passive film, the corrosion rate increases rapidly. Therefore, the surface temperature of the metal should be determined during process operation. The inner diameter of the tubing gets hotter as the hot wall impacts the re-boiler tubing. As a result, the rate of corrosion is higher than expected.
- Coating:
Coatings protect against erosion and corrosion by shielding the material from several chemical and physical damages that occur due to direct contact of material with the environment. As corrosion results in dilapidation, it causes failure of components in biomass boilers. The coating improves surfaces against corrosion and deposits suitable material on the substrate.
Operational Challenges of Biomass Boilers:
- Availability of biomass and storage problem
- Difficulty with transportation due to moisture content of biomass fuel
- Inefficient fuel conversion, core technology, and equipment
- Industrial chain
Economic Challenges of Biomass Boilers:
- Cost of Feedstock acquisition
- High investment and capital cost
Social Challenges of Biomass Boilers:
- Issues with land use
- Impact on the environment with loss of biodiversity
Policy and Regulatory Challenges of Biomass Boilers:
- Government Policies
- Lack of Special Department for Biomass
Conclusion:
One of the major issues related to biomass fuel is the energy density and moisture content. For instance, 30% moisture in conventional wood means that 1 ton of wood contains 300 kg. of water. Additionally, process industries need to ensure fuel conversion of the steam boiler before utilizing biomass fuel.
Over the last 38+ years, Rakhoh Boilers have emerged as a leading steam boiler manufacturer in Pune by delivering efficient industrial steam boilers in 26 countries worldwide. We also provide excellent boiler services like fuel conversion, energy audit, steam trap assessment, boiler automation, annual boiler maintenance, etc.
To learn more about our products and services, visit www.rakhoh.com
- Published in Boiler
A Guide to Biomass Boilers | Working, Fuel Types, Advantages, and Disadvantages
Steam Boilers are undoubtedly an essential asset in most process and manufacturing industries. Fuels play a vital role in the combustion process of steam boilers. The ignition of fuel heats the water that causes vaporization to generate steam. Steam boiler varies with the fuels used by the process plant, such as solid fuel boilers, oil-fired boilers, gas-fired boilers, and biomass boilers. The increasing costs of fuels that consequently increase the production costs as well as environmental laws have escalated the demand for biomass boilers in recent years. Biomass boilers are emerging as an ideal solution for heating sustainably and efficiently. Let us have a detailed understanding of the working of biomass boilers along with their advantages and disadvantages.
What is a Biomass Boiler?
Biomass boilers are an ideal choice for renewable heating. For understanding biomass boilers, it is necessary to understand the concept of biomass. Biomass is a fuel acquired from organic matter such as wood, agricultural wastes, industrial wastes, etc. Such renewable steam boiler systems are available for various types of biomass fuel with a range of product capacity, depending on the requirements of the process plant. With the increasing costs of non-renewable fuels like coal and the depletion of fossil fuels in the next three to four decades, biomass boilers are the best solution for effective heating and steam generation.
In other words, biomass boilers offer heating from renewable fuels, efficient steam generation, and reduce greenhouse emissions.
Biomass Conversion into Energy:
Biomass can be converted into energy through various processes such as,
- Direct Combustion: Burning the fuel to produce heat. Direct combustion is the most commonly used method of converting biomass into energy. Biomass of any type is burned for heating in industries, buildings, and generating electricity through steam turbines.
- Thermochemical: The process involves conversion to produce solid, liquid, or gaseous fuels. Thermochemical conversion involves the process of pyrolysis and gasification that are decomposition processes. It includes heating the biomass feedstock materials at high temperatures in closed, pressurized vessels termed gasifiers.
- Chemical: Chemical conversion produces liquid fuels. Also known as transesterification, it is used for converting animal fats, vegetable oils, and greases into fatty acid methyl esters (FAME), utilized for producing biodiesel.
- Biological: It includes biomass conversion into producing liquid and gaseous fuels. Biological conversion involves fermentation in order to convert biomass into ethanol and anaerobic digestion that resultantly produces renewable natural gas. Renewable natural gas, also termed biogas or biomethane, is generated in anaerobic digesters at sewage treatment plants or dairy or livestock operations. It can also be captured and produced from solid waste landfills. If treated properly, renewable natural gas has the same utilization as fossil fuel natural gas.
Working of Biomass Boilers:
One of the primary benefits of adapting to biomass boilers is their ease of use. Like general steam boilers, biomass boilers use renewable fuels like wood, wood chips, wood pellets, agricultural wastes, industrial wastes, etc., to generate heat for steam.
Biomass boilers operate by burning the fuels suited for the steam boiler system, utilized for heating to generate steam. However, biomass boilers require a larger amount of fuel compared to fossil fuels. Biomass boilers are easy to maintain, but the ash built up by burning the fuel requires regular cleaning.
Types of Biomass Fuels:
Some of the most commonly used biomass fuels are as follows,
- Wood Chips:
Wood chips are the most economical type of biomass fuel that produces around 2.5p per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity. It consists of a 30% moisture content that should not be stored for longer periods to avoid degradation. The drawback of using wood chips is the germination of spores that can cause incurable respiratory disease. Therefore, it is essential to keep the airflow and encourage the drying process.
- Wood Pellets:
Wood pellets are relatively expensive, as compared to wood chips. It is the densest form of biomass, as well as efficient and compact. Wood pellets release a high amount of dust that requires effective hoppers and dust collector systems.
- Wood Logs:
Wood logs are ideal for those having access to wood sources and large storage spaces. Due to its high moisture content, it requires to be stored in a dry place for a year to reduce its moisture content and allow its maximum efficiency. It can also be used as wood bark and sawdust.
- Agricultural Wastes:
Agricultural wastes such as briquettes, bailed bagasse, rice husk, coffee husk, palm shell, groundnut shell, coconut shell, cotton waste, etc. It is best-suited to agricultural industries and industries that can transport the fuels conveniently and store them easily.
- Industrial Wastes:
Industrial wastes like paper pulp, wood waste, textile waste, etc. can be used as fuels depending on the requirement and capacity of the steam boiler system.
Advantages of Biomass Boilers:
- Environment-friendly
- Renewable source of energy
- Cost-effective
- Easy to procure and transport
Disadvantages of Biomass Boilers:
- Requires large space for storage
- Requires Large Furnace
Efficient Biomass Boilers by Rakhoh:
With 38+ years of expertise and experience in thermal solutions, Rakhoh Boilers have aimed to balance advancement and sustainability with consistent innovations. We deliver efficient and reliable Biomass Boilers that operate effectively with various types of biomass fuels. As a leading steam boiler provider globally, we provide the best boiler services like fuel conversion, boiler automation, energy audit, annual boiler maintenance, steam trap assessment, turnkey solutions, etc.
Learn more about our products and services on www.rakhoh.com
- Published in Boiler