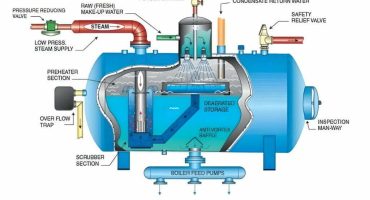
Direct Method and Indirect Method Testing of Efficiency in Boilers
Efficiency is an important factor in evaluating the performance of the boiler. The overall boiler efficiency depends on the efficiency of the various other components. The boiler efficiency is mainly determined by its combustion and thermal efficiency. It can be affected by some other losses as well.
Combustion Efficiency:
The combustion efficiency determines the burner’s ability to burn the fuel. The combustion efficiency is indicated by the amount of unburned fuel and oxygen level in the exhaust. Combustion efficiency depends on the fuel burned and is higher for liquid and gaseous fuels than solid fuels.
Thermal Efficiency:
Thermal efficiency indicates the effectiveness of the heat exchanger to transfer the heat energy in the boiler. Scaling and soot formation on boiler tubes negatively impact thermal efficiency.
Boiler Efficiency Testing:
Apart from combustion efficiency and thermal efficiency, other parameters affect the overall efficiency, such as blowdown losses, on-off losses, convection losses, radiation losses, etc. Boiler efficiency is calculated through two methods,
Direct Method: The direct method of testing boiler efficiency involves comparing the energy of the fluid (water and steam) with the fuel energy
Indirect Method: The indirect method of testing efficiency determines the difference between the losses and the energy input in the boiler
Direct Method of Testing Boiler Efficiency:
The direct method is also termed as input-output method as it only requires output (steam) and input (fuel) to assess the boiler efficiency and can be calculated by the following formula,
Boiler Efficiency = (Heat Output/Heat Input) x 100
Measurements Required for Direct Method Testing of Efficiency:
Heat Input:
Both heat input and heat output are imperative for calculating efficiency. Heat input measurement requires the calorific value of the fuel and its flow rate in terms of mass or volume, depending on the fuel.
Solid fuel: Measuring an accurate flow rate of coal or any other solid fuel is challenging. Measurement based on mass requires an apparatus set-up in the boiler house. The sample bags are sealed and sent to laboratories for testing.
Liquid fuel: Heavy fuel oil is viscous that causes it to vary with temperature. The meter installed in the combustion appliance provides approximate results, and it is advisable to use a calibrated meter for the particular fuel.
Gaseous fuel: A gas meter used requires the measured volume to be corrected for temperature and pressure.
Heat Output:
Various methods are used to measure heat output. Steam boilers use the installed steam meter to measure the flow rate. With small boilers, feed water can be measured by calibrating the feed tank. Heat addition used for conversion of feed water to inlet steam must be considered for heat output. Additionally, the heat loss during continuous blowdown should be calculated and included in the steam heat.
Advantages of Direct Method of Testing Boiler Efficiency:
- Quick evaluation of efficiency
- Needs few factors for calculation
- Requires less instruments for testing
Disadvantages of Direct Method of Testing Boiler Efficiency:
- Causes of low efficiency remain unspecified
- Does not calculate various losses at different stages
- Wet steam due to carryover may lead to incorrect evaporation ratio and efficiency
Indirect Method of Testing Boiler Efficiency:
The indirect method includes measuring all the losses that take place in the boiler. The efficiency is calculated by subtracting heat loss from 100. Unlike the direct method, slight measurement errors would not significantly change the efficiency rate in the indirect method. The various types of heat losses in boilers are losses due to hydrogen in fuel, dry fuel gas, moisture in fuel, carbon monoxide, air moisture, convection, surface radiation, unburned losses in fly ash and bottom ash, etc.
Boiler efficiency can be calculated by the indirect method of testing with the following formula,
100 – Losses occurred in the boiler
Measurements Required for Indirect Method of Testing Boiler Efficiency:
The parameters required to measure boiler efficiency through the indirect method are as follows,
- Flue gas analysis in terms of percentage of carbon dioxide, oxygen, and carbon monoxide in flue gas, and temperature of flue gas
- Flowmeter measurements for feed water, condensate water, fuel, steam, and combustion air
- Temperature measurements for fuel, makeup water, steam, flue gas, combustion air, feed water, and condensate return
- Pressure measurements for fuel, steam, draft, and combustion air (primary and secondary)
- Water conditions for Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), Blowdown rate, and pH
Advantages of Indirect Method of Testing Boiler Efficiency:
- Complete balance between mass and energy for individual stream
- Alternatives to improve boiler efficiency are identified
Disadvantages of Indirect Method of Testing Boiler Efficiency:
- Requires considerable time
- Needs lab settings for analysis
Factors that improve boiler efficiency:
- Regular maintenance of boilers
- Excess air control
- Quality of Fuel
- Boiler insulation
- Proper water treatment
- Optimal steam pressure and temperature
Rakhoh Boilers are one of the reputed steam boiler manufacturers and service providers in India and worldwide. With 38+ years of experience, we deliver world-class quality boilers and the best boiler services to our clients for enhancing efficiency and productivity. To learn more about our products and services, visit www.rakhoh.com
- Published in Boiler
Tips to Increase Steam Boiler Efficiency
Manufacturing and process industries require steam for various process operations. Therefore, boilers are imperative for generating high-quality steam to accomplish operational purposes in the processing facilities. One of the most important factors to consider before investing in a steam boiler is boiler efficiency. Boiler efficiency can be termed as the ratio of the useful heat output to the total energy input. The majority of heat lost in the steam boiler is in the boiler water or stack. The process plant can significantly increase its boiler efficiency by following some practices, consequently reducing excess costs.
15 Practices to Increase Boiler Efficiency:
- Regular Tuning of the Burner:
The right amount of air is one of the factors that impact boiler efficiency. A certain amount of oxygen is essential for the proper combustion of fuels. In case of air being too low, the carbon in the fuel starts to oxidize, leading to the formation of carbon monoxide. It results in the release of heat in a reduced amount as the fuel is not burned completely. Soot, smoke, and carbon monoxide are caused due to low air that causes harm to the boiler. Excess air also decreases boiler efficiency as it is transported to the stack hot that wastes heat.
An optimum amount of air ensures proper and complete combustion of the fuel. For proper combustion, the amount of air needs to be measured with an O2 probe. The probe is inserted in the stack while tuning the burner for optimal boiler efficiency. Tuning the burners regularly results in maximum savings of fuel.
- Reduce the Stack Temperature:
Reducing stack temperature is an easy process that decreases the operating pressure when the steam boiler is not in operation.
- Proper Insulation of Valves:
Insulation plays a crucial role in capturing heat and preventing its wastage. Neglecting the insulation after maintenance can cause tremendous heat loss. Insulating valves helps in avoiding heat loss, reducing accidents, and ensuring easy access for maintenance. Optimal use of heat, in turn, increases the boiler efficiency.
- Using an Economizer:
Economizers utilize the wasted hot flue gas and heat the feed water for combustion purposes in a steam boiler. Installing an economizer can significantly reduce the fuel consumption for heating the water, thereby increasing the boiler efficiency.
- Cleaning of Fireside:
As the boiler age advances, the soot layers start forming on the fireside of the boiler tubes that act as an insulator. Consequently, it reduces the heat transfer rate and increases fuel usage. Due to the low heat transfer rate, the hot gases pass without transmitting heat to the water. It resultantly increases the stack temperature and decreases the overall boiler efficiency. Therefore, it is necessary to inspect and clean the fireside of the steam boiler to prevent soot formation.
- Cleaning of Waterside:
It is pivotal to thoroughly check the waterside to ensure that there are no leakages or scale formation. Scaling forms on the heat transfer surfaces due to improper chemical treatment, high levels of water hardness, and irregular blowdown. It results in hindering the heat transfer that eventually reducing the boiler efficiency. If overlooked, scaling can cause overheating in boilers that lead to expensive boiler repairs.
- Boiler Blowdown:
Boiler efficiency can be increased by recovering heat from the blowdown process. The blowdown valve helps in releasing the boiler water containing soluble and insoluble solids. It reduces the number of dissolved solids that impede the heat transfer process.
- Controlling Blowdown Rate:
Although blowdown removes the impurities from the steam boiler, it also discharges heat from the boiler system. It is crucial to maintain the rate of heat drained through blowdown. The required amount of blowdown can be ensured by installing an automatic blowdown valve.
- Return Condensate to the Boiler:
Condensate is the result of steam transmitting its heat and condensing. The by-product is utilized with already heated water that requires less fuel to generate steam again. Reusing the condensate also reduces the amount of makeup water and chemical treatment required.
- Preheating Combustion Air:
If the air feed in the boiler for combustion is already heated, it requires less fuel to generate steam. A 40 °F increase in the air used for combustion can save up to 1% fuel costs.
- Retrofitting Burners:
Steam boilers require air for proper and complete combustion. Too little air or too much air affects the combustion process, thereby reducing the overall boiler efficiency. Retrofitting and upgrading to a high-efficiency burner is a better option compared to tuning the burners. Retrofitting is an ideal solution for burners that are more than 15 years old. Burner upgrading can save up to 20% of fuel costs.
- Reduce Carryover:
Carryover is caused by water leaving the boiler system along with steam. The wet steam carries impurities like dissolved solids with it. The impurities leave deposits in the boiler system that impacts boiler parts such as control valves and pressure regulators. It results in damage in steam boilers that affects their efficiency.
- Inspection of Steam Trap:
A broken or damaged steam trap allows steam to blow away into the condensate system. Therefore, it is important to regularly inspect the steam trap and replace it if broken to ensure maximum efficiency.
- Avoid Excessive Use of Steam:
Reducing steam usage can significantly increase boiler efficiency. Insulating the pipes and tanks heated by steam decreases steam utilization and consequently fuel usage. A high-pressure condensate system can reduce the steam used at the deaerator and fuel requirement in the boiler.
- Regular Maintenance of Boiler:
Despite following precaution and standard guidelines in operating steam boiler systems, issues like corrosion, scaling, foaming, etc., are inevitable in the boiler system. It is vital to conduct boiler maintenance regularly to obtain peak efficiency.
Rakhoh Boilers is a leading name in industrial steam boiler manufacturer and thermal solutions since 1983. We have successfully installed 3000+ boilers in 26 countries worldwide for over 20 process industries. We manufacture robust steam boilers and provide the best boiler services to enhance boiler efficiency and productivity.
To learn more about our products and services, visit www.rakhoh.com
- Published in Boiler