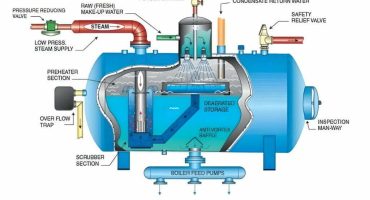
Preventive Maintenance and Cleaning of Biomass Boilers
Biomass boilers are emerging as the future of thermal solutions in the process and manufacturing industries. Boiler maintenance is an important factor to ensure hassle-free operations and optimum efficiency. In the case of biomass boilers, regular maintenance is essential to prevent the breakdown of the boiler. Regular maintenance of biomass boilers cannot be neglected as it may cause severe damage to the boiler system. It is interesting to note that the maintenance of biomass boilers varies from other conventional fossil fuel boilers due to the disposal of the ash produced in the combustion process.
Cleaning and Maintenance of Biomass Boilers:
An ideal way to assess whether the biomass boiler needs cleaning is by examining the increase in fuel consumption. The primary cause of an increase in fuel consumption is due to ash blocking the open airways of the heat exchanger and reduction of the transition of heat in the heating system.
As per the fuel quality, biomass combustion can lead to 0.5-1.5% of their weight in ash, which is released in an ash pan located beneath the grate. The ash collected needs to be removed manually at regular intervals after necessary operational cycles. The boiler maintenance intervals differ depending on the frequency of biomass boilers used for heating. Automatic de-ash systems are used to release the ash into an ash bin, thereby reducing the required amount of workload. However, the ash bin requires it to be emptied from time to time.
Another benefit of biomass boilers is that the collected ash can be used further as a fertilizer. Additionally, the chimney should be cleaned at least once every year.
Disposing Ash in Biomass Boilers:
Ash is the primary by-product of the combustion of biomass fuel. The ash generated by biomass fuel is termed potash. It is useful for the farmers as a top dressing and also for horticulturalists as a component of their compost.
Dispensing ash in such a method is highly beneficial to the environment as the nutrients from the ash are fed to aid in regenerating the wood, collected to form the fuel in the first place. It leads to the increasing popularity of biomass fuels with a boost towards the planting of trees.
Biomass boiler ash can either be disposed of as a fertilizer or landfill waste if the ash is produced in small amounts.
Biomass boilers equipped with automatic ash extraction systems usually include,
Internal ash extraction:
It includes one or more augers that pass ash from the combustion chamber into an ash pan or an external ash auger.
External ash extraction:
It includes one or more ash augers that collect ash from the internal ash augers, emptying itself into a self-contained ash bin.
Fire tube pneumatic cleaning:
It includes various hoses or pipes that automatically pass a blast of compressed air through fire tubes located on the last pass of a three-pass biomass boiler system. It is also termed as the boiler’s ‘tube nest.’
Biomass boilers equipped with the ash extraction system require a daily inspection of the boiler room. The boiler operator inspects the boiler thoroughly to ensure that the combustion levels and flue gas temperatures are within determined limits. The time required for boiler maintenance depends on the size of the boiler, fuel type, and rate of consumption.
Biomass boilers without automatic ash extraction systems need frequent shutdown and need manual servicing. The added cost of boiler maintenance and workload directly impacts by reducing fuel savings and job performance. On the other hand, biomass boilers with automatic ash extraction and tube cleaning increase the boiler performance, efficiency, and lifespan. Therefore, it is important to keep the fire tubes clean of ash for optimal efficiency. As the ash accumulates in the tubes, it acts as an insulator for heat transfer. It results in wasting the heat in the exhaust instead of exchanging it into the boiler water.
Biomass Boiler Maintenance:
Regular maintenance of a biomass boiler ensures a longer life span compared to the conventional fossil boiler system. It leads to internal combustion parts lasting long and less consumption of fuel.
Components Assessed During Biomass Boiler Maintenance:
- The internals of the heat exchanger are examined and cleaned of carbon build-up.
- The boiler and bunker feed screws are assessed and cleaned.
- Geared motor units, bearings, and seals are inspected and greased if necessary.
- Checking every safety equipment.
- Checking the ignition system.
Conclusion:
Rakhoh Boilers, are one of the trusted boiler manufacturers in India, with more than 3000 successful boiler installations in over 26 countries worldwide. We manufacture a range of efficient steam boilers that provide effective combustion with biomass boilers. We deliver waste heat recovery systems, thermic fluid heaters, boiler accessories, and various boiler services to over 20 process industries.
Visit www.rakhoh.com to learn more about our products and services.
- Published in Boiler
Why is Steam Boiler Maintenance Important? Brief Overview on Impacts of Negligence of Maintenance
Steam boilers are unarguably an important asset in various manufacturing and processing industries. Boiler maintenance is essential to assure optimal efficiency and performance of the steam boiler system. Steam boilers burn fuel to generate steam by transferring the heat to water. With various advancements, an extensive variety of steam boilers are available, depending on the industrial requirement, fuel availability, area, etc. Regular maintenance of steam boilers is crucial to prevent boiler failures or other mishaps that may cause harm to the process plant and the operating team due to negligence.
Common Issues in Steam Boiler due to Lack of Maintenance:
Boiler Failures:
Boiler failures are generally caused by low water levels, fuel explosion, or poor feedwater quality. It may result in threatening the safety of the process plant and operating personnel.
Fuel Explosions:
One of the most hazardous effects of boiler maintenance negligence is fuel explosion. Fuel explosions can be prevented, with proper operating techniques and timely maintenance.
Low Water Level:
The boiler temperature rises tremendously after combustion, and water is an essential factor that contributes to withstand it. Low water levels can lead to the damaging or melting of steel tubes during the extremely high temperature of the boiler. Modular designed steam boilers install low-water trip switches to monitor the water level. However, even low-water trips cannot entirely ensure optimal water levels because the water in the steam boiler is an unstable mixture of water and steam bubbles. The water level varies with the shrinking and swelling due to pressure changes, firing rate changes, and while adding cold feedwater.
Feedwater Quality:
Feedwater treatment eliminates two factors that cause problems in steam boilers, i.e., solid deposition on the waterside and corrosion. The water in the boiler is vaporized to steam and deposits solid in the form of scale or buildup in the heat transfer area. Scale buildup results in producing an insulating layer that hinders the ability of water to absorb heat from the tube surface. If overlooked for long, it results in localized overheating of the tube and eventually, boiler failure.
Additionally, low water levels or poor water quality may lead to a steam explosion occurring because of overheated parts’ sudden failure under high pressure. A steam explosion can result in ambient conditions of extreme heat and reduce the oxygen level below the survivable limit.
Maintaining boiler feedwater quality prevents deposit formation. High operating pressure and temperature in the steam boiler require stringent feedwater quality. Turbines and superheaters or with higher temperatures require complex feedwater treatment such as osmosis or demineralizer systems.
Feedwater contaminates include oxygen, oil, excess chemicals used in water treatment, various metals, and chemical compounds. Low feedwater quality and the resulting corrosion can cause damage steadily or sudden mishap. The presence of either acid or caustic in boilers can lead to damaging consequences. These chemicals are introduced in boilers due to malfunction, boiler failure, poor water treatment, poor training, and operation.
Regular and efficient boiler maintenance can significantly reduce the possibility of any damage in steam boilers. Additionally, proper monitoring of feedwater quality can alert the operating personnel of any forthcoming dangers thereby, ensuring their safety.
Improper Blowdown:
Efficient blowdown practices are crucial in maintaining high-quality boiler water. Proper continuous blowdown and regular intermittent blowdown reduce the concentration of undesired solids in the steam boiler. The objective of blowdown practice is to maintain the solid concentration in boiler water within acceptable limits.
The blowdown rate depends on various factors such as total dissolved solids, silica, suspended solids, and alkalinity. Boiler water exceeding the determined limits may result in scale and sludge formation, moisture carryover due to foaming, corrosion, and poor performance of steam drum separation. Intermittent blowdowns are ideally performed for immediately reducing the solid concentrations in the boiler water.
Blowdown practices must take place with precision and care. Poor blowdown practices may lead to failure in regular blowdown of the boiler water columns to ensure proper operation of the low-water trip devices.
Factors to Inspect in Boiler Maintenance:
Negligence of boiler maintenance has far-reaching consequences that can cause tremendous harm to the property and person of the manufacturing unit. Here are some of the vital factors that must be checked thoroughly during boiler maintenance.
Regular inspection of safety equipment such as safety valves, gas/fuel train valves, etc., is the first protection against major boiler failure. Although they are checked during annual maintenance, it is advisable to regularly assess their performance to prevent any problems due to pressure vessels.
Assessing the boiler operating pressure and temperature as well as stack temperature is necessary to maintain the boiler efficiency. Boiler exhaust temperature higher than 50°-100°F above the steam temperature requires checking of boiler internals to prevent any scale formation that would reduce the heat transfer rate and cause boiler tube failures.
Inspecting feedwater pressure and temperature lets the operator know about any changes in the proper feedwater system operation. When the pressure or temperature exceeds the expected range, it hinders the feedwater from entering the boiler, causing thermal shock. Depending on the operating pressure and temperature, a crack in the feedwater coupling and boiler shell leads to the emission of harmful fluids and vapors. It endangers the health and safety of the operating team.
Checking the flame through the sight glass is necessary to ensure proper combustion. Poor combustion results in boiler system failure or boiler explosion.
Evaluating the feedwater treatment prevents boiler inefficiencies, improper operation, damaged conditions, and boiler failures. Negligence in maintaining the feedwater quality leads to overheating of boiler tubes and corrosion of the boiler metal.
Rakhoh Boilers has emerged as a leading steam boiler manufacturer since its inception in 1983. We have provided efficient boilers to over 26 countries worldwide, along with the best boiler services like annual boiler maintenance, energy audit, steam trap assessment, boiler automation, etc.
To know more about our products and services, visit www.rakhoh.com
- Published in Boiler