Steam boilers are one of the most important devices required for the seamless operation in any processing plant and industry. Therefore, it is an essential factor for the boiler manufacturers that the boilers are well-maintained for their smooth running and long-lasting performance. Blowdown is a vital step to avoid suspended solids and sludge in the boiler and to generate high-quality steam.
What is Blow Down?
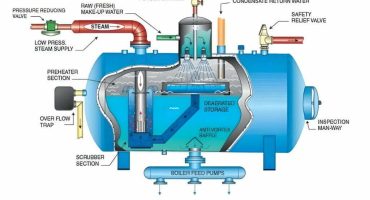
When the boiler is operating, the feedwater contains a high level of Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) along with other dissolved and undissolved solids. These dissolved solids are unable to evaporate once the steam is generated, which results in their settling on the bottom of the boiler shell. It leads to an interruption in the transfer of heat between flue gases and water, eventually resulting in the overheating of the boiler tubes or shell. These undissolved solids may also cause corrosion, scaling, and carryover of solids along with the steam.
Types of Blowdown in Boilers:
As per the design and capacity of the steam boiler and the characteristics of the boiler water, blowdown can be conducted in two ways:
Continuous Blowdown:
Continuous blowdown means when the blowdown is conducted automatically and constantly to maintain the suspended and dissolved solids at their required limit. Continuous blowdown assists in separating a larger amount of dissolved solids through only a slight loss of heat and water from the steam boiler. Moreover, with continuous blowdown, the heat of the water is further used to preheat the feed water with the help of a heat exchanger. In continuous blowdown, the quality of the boiler water is monitored constantly and the blowdown takes place as soon as the TDS level exceeds the optimal limit.
Manual Blowdown:
Manual blowdown is the blowdown conducted manually by operating staff at regular intervals. Manual blowdown helps to separate the sediments and the suspended solids from the steam boiler by opening the valves frequently to conduct blowdowns. In manual blowdown, only a slight opening of the valve is preferred to ensure minimal heat loss. It eventually results in high pressure and heat loss in the steam boiler.
The boiler manufacturers in India and across the world provide the required accessories and valves as per the blowdown operation viz. continuous blowdown or manual blowdown.
Sources of Blowdown in a Steam Boiler:
There are two sources of blowdown found in a steam boiler– bottom blowdown and surface blowdown.
Bottom Blowdown:
Sediments are found in the bottom of the fire tube boilers and inside the mud drum in a water tube boiler. With bottom blowdown, sediments or sludge are separated in regular intervals. It makes sure that it does not contaminate the heat transfer surfaces that result in boiler vessel failure or boiler tube failure. Bottom blowdown occurs by manually opening the concerned valve or valves for a determined period to allow the sludge to exit from the steam boiler. Boiler manufacturers suggest that the bottom blowdown should ideally occur once a day or once in an operational cycle.
Surface Blowdown:
Surface blowdown aids in separating the suspended solids in the boiler water surface. Surface blowdown highly depends on the quality of the water used in the boiler. Therefore, if the water requires a high amount of chemical treatments and contains a higher level of impurities, then it increases the need for surface blowdown.
Boiler manufacturers advise that during blowdown, water needs to be released when its TDS level increases, followed by feeding fresh water in the steam boiler, which leads to the loss of usable heat that is drained out. It results in a reduction in the water temperature and an increase in fuel usage. In this way, blowdown affects the steam fuel ratio of a steam boiler.
Despite that, blowdown has its fair share of advantages and disadvantages.
-
Advantages of Blowdown:
- With the blowdown, the TDS can be kept to an optimal level.
- Blowdown prevents corrosion by removing the impurities that encourage its formation in a steam boiler.
- It prevents carryover of impurities from steam thereby, facilitating the generation of pure steam.
- It prevents scaling in the boiler tubes as well as in the internal surface
-
Disadvantages of Blowdown:
- Neglecting the proper scheduling for blowdown may result in an escalation in heat and pressure losses.
- Eventual reduction in boiler efficiency due to high heat and pressure loss
- Manual blowdown requires additional hours to perform the operation
The formula for calculating boiler blowdown and blowdown percentage:
Boiler manufacturers generally use the following formula to determine boiler blowdown rate and its percentage.
Calculating boiler blowdown rate,
qBD = qS fc / (bc – fc)
Where,
qBD: Blowdown rate in kg/h
qS: Steam Consumption in kg/h
fc: Total Dissolved Solids in feedwater in ppm
bc: Maximum limit of Total Dissolved Solids in boiler water in ppm
Calculating boiler blowdown percentage,
Percent or % of Blowdown = Quantity blowdown water/Quantity feed water X 100
Rakhoh is one of the leading boiler manufacturers in India. With our dedicated team of experts, we have been manufacturing and successfully installing highly efficient boilers for various industries for more than 38 years. We strive to consistently provide advanced steam boilers and excellent boiler-related services to our clients.
Explore our steam boilers and our services on http://www.rakhoh.com