Boiler feedwater is a crucial component for generating steam in manufacturing and processing plants. When water is heated by burning the fuels, it results in steam generation, which is utilized for various operations. Therefore, it is important to ensure that the water used for the process is properly treated and does not contain any contaminants that may negatively impact the steam quality and boiler performance. Poor quality of feedwater leads to various issues in boilers such as corrosion, scaling, foaming, erosion, and water carryover.
An Introduction to Water Carryover in Boilers:
Water carryover in steam boilers occurs when the steam exiting from the boiler is contaminated with undissolved solids or liquid and vaporous content. Carryover in steam boilers is caused due to incomplete separation of water from the steam and may cause problems like corrosion and water hammer. In general cases, boiler water containing impurities passes to the steam system along with steam. It can also cause the formation of deposits on valves, superheaters, turbines, and heat exchangers. Significant deposits reduce heat transfer and turbine efficiency. Water carryover must be prevented at the earliest opportunity. If left unchecked, it causes a loss of efficiency due to wet steam.
Causes of Water Carryover:
Causes of water carryover are categorized into two types, i.e., mechanical causes and chemical causes. They are further classified as the following:
Mechanical Causes of Water Carryover:
Fluctuating Load:
With the fluctuations in boiler load, the possibility of water carryover increases. As the steam demand increases, the steam pressure reduces. It leads to the sudden expansion of drum water known as priming. Priming, in turn, results in slugs of water being carried with the steam that leads to carryover.
Operating Pressure:
Steam boiler, when operated at a lower pressure than its design pressure, causes carryover. As the steam pressure decreases, the specific volume of steam increases. It would lead to higher steam velocity in drum intervals at lower pressure. That hinders the separation of water droplets from steam, consequently leading to water carryover.
Size of the Drum:
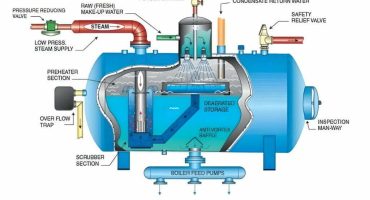
The size of the drum is an important factor for carryover. The steam boilers are designed as per the steam demand. The design of small-diameter drums is enabled with three-element drum level control. The drum internals include cyclone type separators, baffle plates, screen driers, and perforated boxes. The diameter should ensure sufficient distance between the water-steam interface and driers to prevent water carryover.
Arrangement of Drum Internals:
Although there is no specific or standard procedure to arrange the drum internals, the configuration of steam boilers requires variation in drum internals arrangement. Inappropriate drum internal arrangement can be a major cause of carryover.
Erecting of Drum Internals:
Despite every care taken by the boiler manufacturer, erecting a steam boiler at the site may bring difficulties. The drum internals may fail because of corrosion due to low water quality that may lead to carryover.
High Water Level:
While the steam boilers are operating, it must be ensured that all the tripping in the boiler is properly functioning. The boiler manufacturer determines the operating level, alarm level, low water level, and high water level. The low water level impacts the circulation, and the high water level impacts the steam purity. Therefore, the chances of carryover are more with high water levels.
Improper Blowdown:
Continuous blowdown is an ideal method of maintaining the boiler water chemistry. Improper blowdown increases the Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) in a steam boiler, consequently resulting in high water carryover.
Chemical Causes of Water Carryover:
Feedwater Chemistry:
The feedwater chemistry must fulfill certain requirements suggested by the boiler manufacturer before feeding it to the steam boiler. Feedwater containing oils or organic matter leads to foaming that eventually results in water carryover. Additionally, feedwater with dissolved iron would lead to foaming as well.
High Total Dissolved Solids (TDS):
Boiler water with high TDS results in increasing the carryover of solids. For reducing the carryover, it is necessary to bring down the TDS level by eliminating the NaOH in the boiler water through coordinated phosphate control. High alkalinity and suspended solids in boiler water increase carryover.
Excess Chemical Treatment:
Water treatment is essential to minimize the possibility of water carryover. However, excess or improper chemical dosage while treating the water disturbs the boiler water chemistry, causing water carryover.
Prevention of Water Carryover in Boilers:
There are various ways to prevent water carryover such as,
- Effective steam separators like baffles, centrifugal separators, mesh demisters, or screens
- Monitor the steam quality by testing the Total Dissolved Solids, Alkalinity, Silica, and Organic Contamination
- Increasing Boiler Blowdown
- Utilizing Boiler water antifoam chemicals
- Seek the guidance of boiler manufacturer in extreme cases
Rakhoh Boilers, with their extensive knowledge and experience in boiler manufacturing and thermal solutions, understand the problems faced by the processing plants and offer comprehensive solutions with their world-class manufacturing of steam boilers and excellent boiler services in over 26 countries worldwide.
To explore our products and services, visit www.rakhoh.com