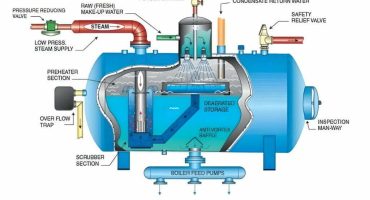
Boilers are the heart of any manufacturing industry, and therefore, the boiler used in process industries must be efficient. Boilers require steam generation for heating purposes in the industry. Boiler efficiency calculates the amount of heat energy converted into steam. Compared to other heat sources, steam is the most preferred one as it is cost-effective for operations and reusable. Yet, despite the many advantages of using steam for heating, boiler operators face many challenges such as corrosion, erosion, steam trap overload, and even boiler shut down due to low water levels. The cause behind most of these boiler problems is poor steam quality.
Steam Quality in Boilers:
Steam Quality can be termed as the amount of liquid contained in the steam. For instance, 100% steam quality refers to steam, without water present in it, and if the steam quality is 80%, then it contains 80% of steam and 20% of water. The water in steam can cause erosion in pipes and valves of the boiler. If water gathers in the steam pipes, it would be carried by high-velocity steam that may lead to vibration, erosion, and water hammer that, in turn, may cause loose pipe fittings, causing boiler shutdown.
Importance of Steam Quality:
It is important to understand that steam is essential for quality manufacturing and hassle-free process operations. Granted, that the steam boiler and its equipment must be regularly checked and maintained. However, in most cases, the steam quality is overlooked. Thus, it is necessary to keep a tab over steam quality to prevent boiler problems and ensure the high quality of the products manufactured through steam.
Effects of Steam Quality on Boiler:
Poor steam quality may lead to harmful consequences in the boiler operation. Here are some of the most commonly found effects of steam quality on boiler:
Failure of the Valves:
The passing of the poor steam quality containing liquid from the steam control valves causes erosion inside the valves that fail the steam valves in boilers.
Failure of the Turbine Components:
Steam consisting of liquid when generated in the turbine operation may reduce the total lifespan of the internal components of the turbine.
Heat Transfer Efficiency:
One of the most occurring problems caused by low steam quality is the reduced heat transfer efficiency in the operational process. It must be noted that poor steam quality can reduce as much as 65% of the heat transfer efficiency.
The liquid contained in the steam has around 16% of sensible energy. However, the latent energy in steam is about 94% which is significantly higher in comparison to sensible energy. It results in less amount of reusable energy being supplied to the steam process equipment. Secondly, the excess liquid in the steam accumulates on the surface of the heat exchanger, causing the formation of a water layer that hinders the transferring of the latent energy to the equipment.
Water Hammer:
Steam tends to condense due to the heat loss in the pipe, forming droplets in the internal walls. As they pass with the steam, they merge as a layer, gravitating towards the bottom of the pipe as the layer begins to thicken. It results in the formation of a slug of water that is dense, incompressible, and contains a high amount of kinetic energy.
Obstruction by the bend in the pipe compels the kinetic energy to convert into pressure energy. It results in pressure shock coming in contact with the obstruction. The effect caused by the slug water and obstruction is termed as water hammer. Water Hammer may considerably reduce the life cycle of the pipes and, in extreme cases, may cause an explosion.
Factors that Determine the Steam Quality:
Various factors determine the steam quality for the boiler operation. Some of them are as follows:
Steam Temperature and Pressure:
The steam temperature and pressure must be appropriate depending on the process industry. Failing that may affect the performance of the boiler.
Quantity:
The quantity of steam used in processing affects the flow rate of heat. The flow rate depends on the sizing of the pipes. Therefore, an improper flow rate may be harmful to the boiler and reduce productivity.
Cleanliness of Steam:
Steam is a crucial element in the process operation and hence, it is necessary to ensure it is clean and prevent the formation of scaling on pipes that leads to increased erosion, reducing the quality of steam.
Dryness of Steam:
Improper chemical treatment of feed water causes priming and carryover to the steam mains that gets settled on the heat transfer surfaces, eventually reducing the boiler efficiency. Also, the presence of liquid in steam results in the formation of scale on the pipes. The high amount of droplets in steam hinders the heat transfer process in the boiler. Therefore it is necessary to ensure the dryness of steam.
How to Measure the Steam Quality in Boilers?
Rakhoh Boilers, with their extensive knowledge and expertise in thermal solutions, advises that steam quality assessment is one of the important factors to consider in ensuring the efficiency and lifespan of the boiler. Here are the ways to measure steam quality:
- Testing the steam quality through Throttling Calorimeter or Ganapathy’s Steam Plant Calculations
- Assessing the steam by opening the steam valve that releases the steam into the atmosphere to provide an estimated steam quality result